See Planetarium Activities for Successful Shows (PASS)
A Planetarium Is…
…a hemispherical domed theater in which images of any sort can be projected on the inside of the dome. They’re great in astronomy for showing objects in the sky as they appear any time of night, any day of the year, from any place on Earth.
If you are lucky, your town or one near you has a planetarium that you can visit. To find and visit the nearest one to you, search a worldwide directory of planetariums such as:
- planetariums-database.org/ or the
- International Planetarium Society (IPS) public directory
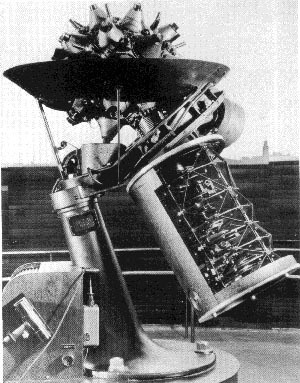
Goto Mercury planetarium projector
at The Lawrence Hall of Science, circa 1978.
The first planetarium star projector
was the Zeiss Mark 1.
Planispheres
A planisphere is a type of star map that is adjustable to show the sky any time of night and any night of the year. In that sense it’s sort of like a hand held planetarium. See the GSS Planisphere page and the GSS investigation Star Maps in A Changing Cosmos.
An interesting way to make an inexpensive planetarium can be found on this web page: A Planetarium for Every Classroom – https://www.cccoe.net/stars/5mdome.html by Jeff Adkins.
Audience Participation in Planetariums
Holt Planetarium at Lawrence Hall of Science (LHS), University of California Berkeley (UCB) was built in 1973 under the direction of Alan Friedman to develop planetarium shows with a novel audience participation style. In the summer of 1978 LHS held five National Science Foundation (NSF)-funded workshops—POP (Participatory Oriented Planetariums)—with 100 planetarium educators.
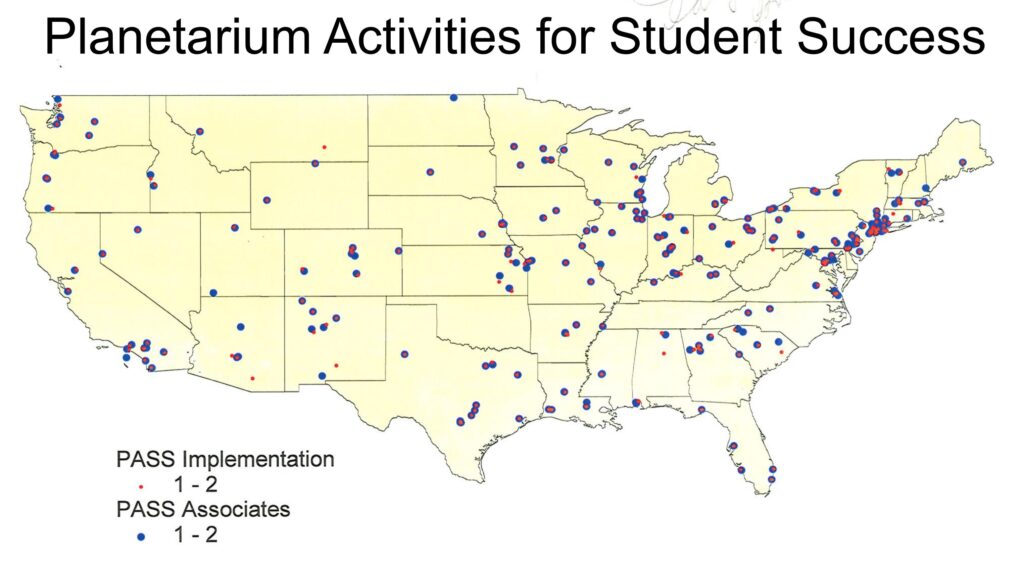
In the summers of 1989-94, LHS recruited a total of 150 participants for six NSF funded Summer Institutes in Astronomy and Space Science Education for Elementary and Middle Schools. The project was POPS—Participatory Oriented Planetariums for Schools). The map below shows where the POPS workshop participants were from.
The POP workshops resulted in a publication, Planetarium Educators Workshop Guide (IPS Special Report #10). The participants/graduates of those institutes conducted in-service workshops in their school districts using an expanded Planetarium Educators Workshop Guide: a series of 12 volumes – Planetarium Activities for Student Success (PASS). Because the audience participation techniques work in both public shows and school shows, the name PASS was changed to Planetarium Activities for Successful Shows. PASS programs are not like pre-recorded products that are simply load-and-play.
The PASS programs are more akin to classroom activities consisting of a written sample narrative as a guide for live presentation, media (still images and movies), materials and preparation (if needed).

With the advent and widespread proliferation of digital planetariums at the beginning of this millennium, the LHS team found that the audience participation principle is as valuable as ever.
Planetarium Activities for Successful Shows (PASS)
Formerly “Planetarium Activities for Student Success”, most of these were developed in pre-digital years (1973-2005) but remain good examples of audience participation strategies.
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
INDEX
- Planetarium Educators Workshop Guide
- Activities for the School Planetarium
- Resources
- A Manual for Using Portable Planetariums
PLANETARIUM PROGRAMS: - Constellations Tonight
- Red Planet Mars
- Moons of the Solar System
- Colors From Space
- How Big Is The Universe?
- Who Discovered America?
- Native American Astronomy
- Stonehenge
- Northern Lights
- Our Very Own Star
- Strange Planets
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 1: Planetarium Educators Workshop Guide
Cover | Contents | Acknowledgments | Introduction

Vol. 1 Appendices
- A Getting a Workshop Together
- B Workshop and Institute Participants
- C An Annotated Bibliography
- D [has become PASS Volumes 5 and 6; or see original appendix D]
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 2: Activities for the School Planetarium
Book Cover | Contents | Acknowledgments
Introduction by Gerald Mallon -|- Introduction by Alan Friedman
About Planetarium Activities

Grades K–2
Grades 3–5
- Light And The Eye
- How Do The Stars Appear To Move
- Plotting The Paths Of Meteors
- Measuring The Brightness Of Stars
Grades 6–9
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 3: Resources for Teaching Astronomy and Space Science
… was a collection of resources from the 1980s, pretty much hopelessly out of date.
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index

Volume 4:
A Manual for Using Portable Planetariums
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 5: Constellations Tonight
(originally in Appendix of Volume 1)
Cover | copyright | contents | introduction | discover more | acknowledgements

Materials-maps | materials-lights | map masters | script tips | media list | using the script
Media: zipped media1 | zipped media 2
Show script sections: find Polaris | sky map activity | making up constellations | big dipper versions | motion of stars | conclusion
Show Activities:
- Finding the Big Dipper
- Using a Sky Map
- Making Up Constellations
- Versions of the Big Dipper
- Motion of the Stars
See also, maps for different latitudes.
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 6: Red Planet Mars
(originally in Appendix of Volume 1)
Cover | copyright | contents | introduction | discover more | acknowledgements

Materials | drawingsheet | media list | setup | using the script
Media: still images, fuzzy mars movie, movies 1–3, valles marineris movie
Show script sections: find red stars | find mars | telescope views | draw mars | lowell | orbit views | surface views | hst | exobiology | sci-fi martian | modern exploration
Show Activities:
See also these related live interactive planetarium shows developed by Jeff Nee at NASA JPL:
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 7: Moons of the Solar Systems
Cover | copyright | contents | intro | discover more | acknowledgements

Materials | materials1 | materials2 | media list | using the script | setup
Media: still images | Movies: moon phases | lunar eclipse | solar eclipse | galilean moons | tour1 | tour2 | tour3 | tour4 | tour5 |
tour-pluto1 | tour-pluto2
Show script sections: observe and explain phases | telescope view | galilean moons | tour of moons | conclusion
Show Activities:
See also Updates to Moons of the Solar System by Jeff Nee.

Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 8: Colors From Space
Materials are in the script booklet
Media: Still Images; Movies; Spectra movie
Show Activities:

Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 9: How Big Is The Universe?
Materials are in the script booklet
Media: Still images; Audio
Show Activities:

Youtube videos with Doppler effect:
https://elements.envato.com/sound-effects/train+doppler
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 10:
Who Discovered America?
Materials are in the script booklet
Media: Still images
Show Activities:

Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 11: Native American Astronomy
(originally Astronomy of the Americas)
Materials are in the script booklet
Media: Still images
Show Activities:

Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index

Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 13: Northern Lights
Script Booklet (with materials) -|- Media: Still images -|- Videos (see list below)
Show Activities:

Media for Northern Lights – Videos:
- 1a Franck’s Narration (part 1) -|- 1b Franck’s Narration (part 2)
- 2 CME
- 3 TRACE
- 4a Iron Filings -|- 4b Solar Wind 1 -|- 4c Solar Wind 2 -|- 4d Aurora
- 5 THEMIS discovery
- 6 Drawing
- 7 Credits
- Aurora from space (.zip) -|- Effects of Solar Storms on Earth
- IMAGE spacecraft -|- THEMIS ground-based All-Sky Imager (ASI) -|- Earth Orbiting Satellites
- Halloween Storms 2003 (.zip) -|- Solar images – multiwave
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 14: Our Very Own Star
Script Booklet (with materials) -|- Media: Still images -|- Videos (see list below) -|- Music
Show Activities:
- Introduction to Our Very Own Star
- The Sun as Timekeeper
- Different Views of the Sun
- Sunspots
- Differential Rotation
- Magnetic Earth – Magnetic Sun
- Conclusion
Media – Videos
- Videos 1 & 7 | 14-19 | 21-25 | 26-30 (.zip files)
- Hinode: Sunspot Cluster
- SDO: Raining Loops A and B
- 3 Years of SDO: A, B, C
- Halloween Storms 2003 (.zip)
- Solar images – multiwave
- Earth Orbiting Satellites

See also: Observing Our Star — a live interactive planetarium show developed by Jeff Nee at NASA JPL.
Volume 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6 – 7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – 13 – 14 – 15 – PASS Index
Volume 15: Strange Planets
- Script Booklet (with materials)
- Media: Still images
- Videos (list below)
- Music: Natalie Pinkis,
Gabriel Liboiron-Cohen
Show Activities:

Media – Videos
- Kepler Launch
- Dust Cover Ejection
- Rainbow
- Wobbling Star
- Spectroscopy
- Hot Jupiter
- Habitable Zone
- Kepler’s 2nd Law
- Orrery
- Orrery Synchronized with Live Lightcurve
- Kepler Orbit A, B, and C
- Transit Light Curve version A, version B
- Diversity of Life A, B, C, and D
- Optical Path
- Transit (orbit inclination)
Kepler 10 minute Mini-Shows
(by Alan Gould, Toshi Komatsu, and Jeff Nee, The Lawrence Hall of Science/UC Berkeley)
Hunting for Water – Presenter Guide (Script) -|- Images
Videos: Life Zone 1 -|- Life Zone 2 -|- Life Zone 3
Inside the Zodiac – Presenter Guide (Script) -|- Images
Videos: Reaction Wheels -|- K2 -|- Kepler Synopsis
Searching for Other Earths – Presenter Guide (Script) -|- Images
Videos: Kepler Launch -|- Kepler Optical Path -|- Light Curve Graph
Planetarium History
The unveiling of the very first planetarium projector was in Jena, Germany in October 1923. It opened to the public with the Deutsches Museum opened in Munich, Germany on May 7, 1925. Centennial celebrations of the invention of the planetarium: 2023–2025. See also: A Brief History of the World’s First Planetarium and the Planetarium Projector Museum website.
Zeiss Mark 1 planetarium projector. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:ZeissMark1.jpg